Section 4.4 — Regression with categorical predictors¶
This notebook contains the code examples from Section 4.4 Regression with categorical predictors from the No Bullshit Guide to Statistics.
Notebook setup¶
In [1]:
Copied!
# Ensure required Python modules are installed
%pip install --quiet numpy scipy seaborn pandas statsmodels ministats
# Ensure required Python modules are installed
%pip install --quiet numpy scipy seaborn pandas statsmodels ministats
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
In [2]:
Copied!
# load Python modules
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# load Python modules
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
In [3]:
Copied!
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
In [4]:
Copied!
# Figures setup
plt.clf() # needed otherwise `sns.set_theme` doesn't work
sns.set_theme(
context="paper",
style="whitegrid",
palette="colorblind",
rc={"font.family": "serif",
"font.serif": ["Palatino", "DejaVu Serif", "serif"],
"figure.figsize": (5, 1.6)},
)
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
# Figures setup
plt.clf() # needed otherwise `sns.set_theme` doesn't work
sns.set_theme(
context="paper",
style="whitegrid",
palette="colorblind",
rc={"font.family": "serif",
"font.serif": ["Palatino", "DejaVu Serif", "serif"],
"figure.figsize": (5, 1.6)},
)
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
<Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
In [5]:
Copied!
# Simple float __repr__
if int(np.__version__.split(".")[0]) >= 2:
np.set_printoptions(legacy='1.25')
# Simple float __repr__
if int(np.__version__.split(".")[0]) >= 2:
np.set_printoptions(legacy='1.25')
In [6]:
Copied!
# Download datasets/ directory if necessary
from ministats import ensure_datasets
ensure_datasets()
# Download datasets/ directory if necessary
from ministats import ensure_datasets
ensure_datasets()
datasets/ directory present and ready.
Definitions¶
Design matrix for linear model lm1¶
In [7]:
Copied!
students = pd.read_csv("datasets/students.csv")
lm1 = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + effort", data=students).fit()
lm1.model.exog[0:3]
students = pd.read_csv("datasets/students.csv")
lm1 = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + effort", data=students).fit()
lm1.model.exog[0:3]
Out[7]:
array([[ 1. , 10.96],
[ 1. , 8.69],
[ 1. , 8.6 ]])
In [8]:
Copied!
students["effort"].values[0:3]
students["effort"].values[0:3]
Out[8]:
array([10.96, 8.69, 8.6 ])
Design matrix for linear model lm2¶
In [9]:
Copied!
doctors = pd.read_csv("datasets/doctors.csv")
formula = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc"
lm2 = smf.ols(formula, data=doctors).fit()
lm2.model.exog[0:3]
doctors = pd.read_csv("datasets/doctors.csv")
formula = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc"
lm2 = smf.ols(formula, data=doctors).fit()
lm2.model.exog[0:3]
Out[9]:
array([[ 1. , 0. , 5. , 0. ],
[ 1. , 20. , 0. , 4.5],
[ 1. , 1. , 0. , 7. ]])
In [10]:
Copied!
doctors[["alc","weed","exrc"]].values[0:3]
doctors[["alc","weed","exrc"]].values[0:3]
Out[10]:
array([[ 0. , 5. , 0. ],
[20. , 0. , 4.5],
[ 1. , 0. , 7. ]])
Example 1: binary predictor variable¶
In [11]:
Copied!
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
lmloc = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=doctors).fit()
lmloc.params
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
lmloc = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=doctors).fit()
lmloc.params
Out[11]:
Intercept 52.956522 C(loc)[T.urb] -6.992885 dtype: float64
In [12]:
Copied!
from ministats.plots.figures import plot_lm_ttest
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(4.6,2.2)}):
ax = plot_lm_ttest(doctors, x="loc", y="score")
ax.set_ylim([25,90])
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper center")
from ministats.plots.figures import plot_lm_ttest
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(4.6,2.2)}):
ax = plot_lm_ttest(doctors, x="loc", y="score")
ax.set_ylim([25,90])
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper center")
In [13]:
Copied!
rur_mean = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="rur"]["score"].mean()
urb_mean = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="urb"]["score"].mean()
rur_mean, urb_mean, urb_mean - rur_mean
rur_mean = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="rur"]["score"].mean()
urb_mean = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="urb"]["score"].mean()
rur_mean, urb_mean, urb_mean - rur_mean
Out[13]:
(52.95652173913044, 45.96363636363636, -6.992885375494076)
Encoding¶
In [14]:
Copied!
doctors["loc"][0:5]
doctors["loc"][0:5]
Out[14]:
0 rur 1 urb 2 urb 3 urb 4 rur Name: loc, dtype: object
In [15]:
Copied!
lmloc.model.exog[0:5]
lmloc.model.exog[0:5]
Out[15]:
array([[1., 0.],
[1., 1.],
[1., 1.],
[1., 1.],
[1., 0.]])
In [16]:
Copied!
# ALT.
# dmatrix("1 + C(loc)", doctors)[0:5]
# ALT.
# dmatrix("1 + C(loc)", doctors)[0:5]
Dummy coding for categorical predictors¶
In [17]:
Copied!
cats = ["A", "B", "C", "C"]
catdf = pd.DataFrame({"cat":cats})
catdf
cats = ["A", "B", "C", "C"]
catdf = pd.DataFrame({"cat":cats})
catdf
Out[17]:
| cat | |
|---|---|
| 0 | A |
| 1 | B |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | C |
In [18]:
Copied!
from patsy import dmatrix
dmatrix("1 + C(cat)", data=catdf)
from patsy import dmatrix
dmatrix("1 + C(cat)", data=catdf)
Out[18]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept C(cat)[T.B] C(cat)[T.C]
1 0 0
1 1 0
1 0 1
1 0 1
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
'C(cat)' (columns 1:3)
Example 2: predictors with three levels¶
In [19]:
Copied!
doctors = pd.read_csv("datasets/doctors.csv")
doctors["work"].head(5)
doctors = pd.read_csv("datasets/doctors.csv")
doctors["work"].head(5)
Out[19]:
0 hos 1 cli 2 hos 3 eld 4 cli Name: work, dtype: object
In [20]:
Copied!
dmatrix("1 + C(work)", data=doctors)[0:5]
dmatrix("1 + C(work)", data=doctors)[0:5]
Out[20]:
array([[1., 0., 1.],
[1., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 1.],
[1., 1., 0.],
[1., 0., 0.]])
In [21]:
Copied!
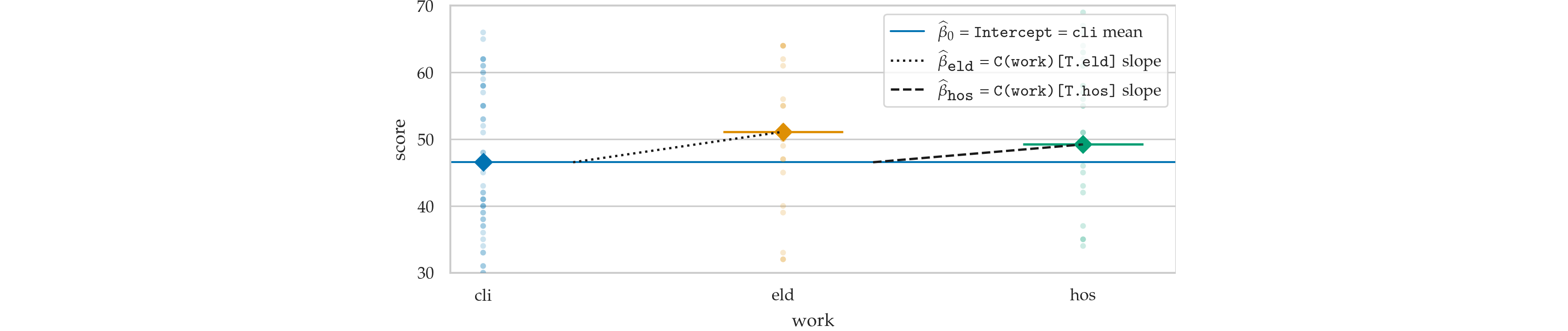
lmw = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(work)", data=doctors).fit()
lmw.params
lmw = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(work)", data=doctors).fit()
lmw.params
Out[21]:
Intercept 46.545455 C(work)[T.eld] 4.569930 C(work)[T.hos] 2.668831 dtype: float64
In [22]:
Copied!
lmw.rsquared
lmw.rsquared
Out[22]:
0.0077217625749193
In [23]:
Copied!
lmw.fvalue, lmw.f_pvalue
lmw.fvalue, lmw.f_pvalue
Out[23]:
(0.5953116925291129, 0.5526627461285702)
Example 3: improved model for the sleep scores¶
We can mix of numerical and categorical predictors
In [24]:
Copied!
formula3 = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc + C(loc)"
lm3 = smf.ols(formula3, data=doctors).fit()
lm3.params
formula3 = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc + C(loc)"
lm3 = smf.ols(formula3, data=doctors).fit()
lm3.params
Out[24]:
Intercept 63.606961 C(loc)[T.urb] -5.002404 alc -1.784915 weed -0.840668 exrc 1.783107 dtype: float64
In [25]:
Copied!
lm3.rsquared, lm3.aic
lm3.rsquared, lm3.aic
Out[25]:
(0.8544615790287665, 1092.5985552344712)
In [26]:
Copied!
from ministats import plot_partreg
plot_partreg(lm3, "alc");
from ministats import plot_partreg
plot_partreg(lm3, "alc");
In [27]:
Copied!
lm3.summary()
lm3.summary()
Out[27]:
| Dep. Variable: | score | R-squared: | 0.854 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model: | OLS | Adj. R-squared: | 0.851 |
| Method: | Least Squares | F-statistic: | 221.6 |
| Date: | Thu, 27 Nov 2025 | Prob (F-statistic): | 4.18e-62 |
| Time: | 09:24:58 | Log-Likelihood: | -541.30 |
| No. Observations: | 156 | AIC: | 1093. |
| Df Residuals: | 151 | BIC: | 1108. |
| Df Model: | 4 | ||
| Covariance Type: | nonrobust |
| coef | std err | t | P>|t| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 63.6070 | 1.524 | 41.734 | 0.000 | 60.596 | 66.618 |
| C(loc)[T.urb] | -5.0024 | 1.401 | -3.572 | 0.000 | -7.770 | -2.235 |
| alc | -1.7849 | 0.068 | -26.424 | 0.000 | -1.918 | -1.651 |
| weed | -0.8407 | 0.462 | -1.821 | 0.071 | -1.753 | 0.071 |
| exrc | 1.7831 | 0.133 | 13.400 | 0.000 | 1.520 | 2.046 |
| Omnibus: | 4.325 | Durbin-Watson: | 1.823 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prob(Omnibus): | 0.115 | Jarque-Bera (JB): | 4.038 |
| Skew: | 0.279 | Prob(JB): | 0.133 |
| Kurtosis: | 3.556 | Cond. No. | 46.2 |
Notes:
[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.
Compare to the model without loc predictor¶
In [28]:
Copied!
formula2 = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc"
lm2 = smf.ols(formula2, data=doctors).fit()
F, p, _ = lm3.compare_f_test(lm2)
F, p
formula2 = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc"
lm2 = smf.ols(formula2, data=doctors).fit()
F, p, _ = lm3.compare_f_test(lm2)
F, p
Out[28]:
(12.758115596295536, 0.00047598123084920574)
Everything is a linear model¶
One-sample t-test as a linear model¶
In [29]:
Copied!
kombucha = pd.read_csv("datasets/kombucha.csv")
ksample04 = kombucha[kombucha["batch"]==4]["volume"]
ksample04.mean()
kombucha = pd.read_csv("datasets/kombucha.csv")
ksample04 = kombucha[kombucha["batch"]==4]["volume"]
ksample04.mean()
Out[29]:
1003.8335
In [30]:
Copied!
from scipy.stats import ttest_1samp
resk = ttest_1samp(ksample04, popmean=1000)
resk.statistic, resk.pvalue
from scipy.stats import ttest_1samp
resk = ttest_1samp(ksample04, popmean=1000)
resk.statistic, resk.pvalue
Out[30]:
(3.087703149420272, 0.0037056653503329626)
In [31]:
Copied!
# # ALT. using the helper function from `ministats`
# from ministats import ttest_mean
# ttest_mean(ksample04, mu0=1000)
# # ALT. using the helper function from `ministats`
# from ministats import ttest_mean
# ttest_mean(ksample04, mu0=1000)
In [32]:
Copied!
# Prepare zero-centered data (volume - 1000)
kdat04 = pd.DataFrame()
kdat04["zcvolume"] = ksample04 - 1000
# Fit linear model with only an intercept term
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
lmk = smf.ols("zcvolume ~ 1", data=kdat04).fit()
lmk.params
# Prepare zero-centered data (volume - 1000)
kdat04 = pd.DataFrame()
kdat04["zcvolume"] = ksample04 - 1000
# Fit linear model with only an intercept term
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
lmk = smf.ols("zcvolume ~ 1", data=kdat04).fit()
lmk.params
Out[32]:
Intercept 3.8335 dtype: float64
In [33]:
Copied!
lmk.tvalues.iloc[0], lmk.pvalues.iloc[0]
lmk.tvalues.iloc[0], lmk.pvalues.iloc[0]
Out[33]:
(3.0877031494203044, 0.0037056653503326335)
Two-sample t-test as a linear model¶
East vs. West electricity prices¶
In [34]:
Copied!
eprices = pd.read_csv("datasets/eprices.csv")
pricesW = eprices[eprices["loc"]=="West"]["price"]
pricesE = eprices[eprices["loc"]=="East"]["price"]
pricesW.mean() - pricesE.mean()
eprices = pd.read_csv("datasets/eprices.csv")
pricesW = eprices[eprices["loc"]=="West"]["price"]
pricesE = eprices[eprices["loc"]=="East"]["price"]
pricesW.mean() - pricesE.mean()
Out[34]:
3.000000000000001
Two-sample t-test with pooled variance¶
In [35]:
Copied!
from scipy.stats import ttest_ind
rese = ttest_ind(pricesW, pricesE, equal_var=True)
rese.statistic, rese.pvalue
from scipy.stats import ttest_ind
rese = ttest_ind(pricesW, pricesE, equal_var=True)
rese.statistic, rese.pvalue
Out[35]:
(5.022875513276465, 0.00012497067987678488)
In [36]:
Copied!
ci_Delta = rese.confidence_interval(confidence_level=0.9)
[ci_Delta.low, ci_Delta.high]
ci_Delta = rese.confidence_interval(confidence_level=0.9)
[ci_Delta.low, ci_Delta.high]
Out[36]:
[1.957240525873166, 4.042759474126836]
Linear model approach¶
In [37]:
Copied!
lme = smf.ols("price ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=eprices).fit()
print(lme.params)
lme.tvalues.iloc[1], lme.pvalues.iloc[1]
lme = smf.ols("price ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=eprices).fit()
print(lme.params)
lme.tvalues.iloc[1], lme.pvalues.iloc[1]
Intercept 6.155556 C(loc)[T.West] 3.000000 dtype: float64
Out[37]:
(5.022875513276466, 0.00012497067987678464)
In [38]:
Copied!
lme.conf_int(alpha=0.1).iloc[1].values
lme.conf_int(alpha=0.1).iloc[1].values
Out[38]:
array([1.95724053, 4.04275947])
In [39]:
Copied!
from ministats.plots.figures import plot_lm_ttest
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(4.2,3.1)}):
ax = plot_lm_ttest(eprices, x="loc", y="price")
ax.set_ylim([4.5,10])
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left")
ax.xaxis.set_label_coords(0.5, -0.07)
from ministats.plots.figures import plot_lm_ttest
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(4.2,3.1)}):
ax = plot_lm_ttest(eprices, x="loc", y="price")
ax.set_ylim([4.5,10])
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left")
ax.xaxis.set_label_coords(0.5, -0.07)
Example 1 (revisited): urban vs. rural doctors¶
In [40]:
Copied!
from scipy.stats import ttest_ind
scoresR = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="rur"]["score"]
scoresU = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="urb"]["score"]
resloc = ttest_ind(scoresU, scoresR, equal_var=True)
resloc.statistic, resloc.pvalue
from scipy.stats import ttest_ind
scoresR = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="rur"]["score"]
scoresU = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="urb"]["score"]
resloc = ttest_ind(scoresU, scoresR, equal_var=True)
resloc.statistic, resloc.pvalue
Out[40]:
(-1.9657612140164198, 0.05112460353979368)
In [41]:
Copied!
lmloc = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=doctors).fit()
lmloc.tvalues.iloc[1], lmloc.pvalues.iloc[1]
lmloc = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=doctors).fit()
lmloc.tvalues.iloc[1], lmloc.pvalues.iloc[1]
Out[41]:
(-1.9657612140164178, 0.05112460353979391)
One-way ANOVA as a linear model¶
In [42]:
Copied!
from scipy.stats import f_oneway
scoresH = doctors[doctors["work"]=="hos"]["score"]
scoresC = doctors[doctors["work"]=="cli"]["score"]
scoresE = doctors[doctors["work"]=="eld"]["score"]
resw = f_oneway(scoresH, scoresC, scoresE)
resw.statistic, resw.pvalue
from scipy.stats import f_oneway
scoresH = doctors[doctors["work"]=="hos"]["score"]
scoresC = doctors[doctors["work"]=="cli"]["score"]
scoresE = doctors[doctors["work"]=="eld"]["score"]
resw = f_oneway(scoresH, scoresC, scoresE)
resw.statistic, resw.pvalue
Out[42]:
(0.5953116925291181, 0.5526627461285608)
In [43]:
Copied!
lmw = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(work)", data=doctors).fit()
print(lmw.params)
lmw.fvalue, lmw.f_pvalue
lmw = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(work)", data=doctors).fit()
print(lmw.params)
lmw.fvalue, lmw.f_pvalue
Intercept 46.545455 C(work)[T.eld] 4.569930 C(work)[T.hos] 2.668831 dtype: float64
Out[43]:
(0.5953116925291129, 0.5526627461285702)
In [44]:
Copied!
from ministats.plots.figures import plot_lm_anova
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(5,3)}):
ax = plot_lm_anova(doctors, x="work", y="score")
ax.set_ylim([31,69])
sns.move_legend(ax, "lower right")
from ministats.plots.figures import plot_lm_anova
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(5,3)}):
ax = plot_lm_anova(doctors, x="work", y="score")
ax.set_ylim([31,69])
sns.move_legend(ax, "lower right")
In [45]:
Copied!
# BONUS: print ANOVA table
# import statsmodels.api as sm
# sm.stats.anova_lm(lmw)
# BONUS: print ANOVA table
# import statsmodels.api as sm
# sm.stats.anova_lm(lmw)
Nonparametric tests¶
One-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test¶
In [46]:
Copied!
kombucha = pd.read_csv("datasets/kombucha.csv")
ksample04 = kombucha[kombucha["batch"]==4]["volume"]
# Zero-centered volumes
zcksample04 = ksample04 - 1000
from scipy.stats import wilcoxon
reswil = wilcoxon(zcksample04)
reswil.pvalue
kombucha = pd.read_csv("datasets/kombucha.csv")
ksample04 = kombucha[kombucha["batch"]==4]["volume"]
# Zero-centered volumes
zcksample04 = ksample04 - 1000
from scipy.stats import wilcoxon
reswil = wilcoxon(zcksample04)
reswil.pvalue
Out[46]:
0.002770629538645153
In [47]:
Copied!
# Create a new data frame with the signed ranks of the volumes
df_zcsr = pd.DataFrame()
df_zcsr["zcvolume_sr"] = np.sign(zcksample04) * zcksample04.abs().rank()
lmwil = smf.ols("zcvolume_sr ~ 1", data=df_zcsr).fit()
lmwil.pvalues.iloc[0]
# Create a new data frame with the signed ranks of the volumes
df_zcsr = pd.DataFrame()
df_zcsr["zcvolume_sr"] = np.sign(zcksample04) * zcksample04.abs().rank()
lmwil = smf.ols("zcvolume_sr ~ 1", data=df_zcsr).fit()
lmwil.pvalues.iloc[0]
Out[47]:
0.0022841508459744125
Mann-Whitney U-test¶
In [48]:
Copied!
scoresR = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="rur"]["score"]
scoresU = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="urb"]["score"]
from scipy.stats import mannwhitneyu
resmwu = mannwhitneyu(scoresU, scoresR)
resmwu.pvalue
scoresR = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="rur"]["score"]
scoresU = doctors[doctors["loc"]=="urb"]["score"]
from scipy.stats import mannwhitneyu
resmwu = mannwhitneyu(scoresU, scoresR)
resmwu.pvalue
Out[48]:
0.05008336985073764
In [49]:
Copied!
# Compute the (unsigned) ranks of the scores
doctors["score_r"] = doctors["score"].rank()
# Fit a linear model
lmmwu = smf.ols("score_r ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=doctors).fit()
lmmwu.pvalues.iloc[1]
# Compute the (unsigned) ranks of the scores
doctors["score_r"] = doctors["score"].rank()
# Fit a linear model
lmmwu = smf.ols("score_r ~ 1 + C(loc)", data=doctors).fit()
lmmwu.pvalues.iloc[1]
Out[49]:
0.049533887469989255
Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance by ranks¶
In [50]:
Copied!
from scipy.stats import kruskal
reskw = kruskal(scoresH, scoresC, scoresE)
reskw.pvalue
from scipy.stats import kruskal
reskw = kruskal(scoresH, scoresC, scoresE)
reskw.pvalue
Out[50]:
0.4441051932875236
In [51]:
Copied!
# Compute the (unsigned) ranks of the scores
doctors["score_r"] = doctors["score"].rank()
lmkw = smf.ols("score_r ~ 1 + C(work)", data=doctors).fit()
lmkw.f_pvalue
# Compute the (unsigned) ranks of the scores
doctors["score_r"] = doctors["score"].rank()
lmkw = smf.ols("score_r ~ 1 + C(work)", data=doctors).fit()
lmkw.f_pvalue
Out[51]:
0.44688872149660885
Explanations¶
Dummy coding options¶
In [52]:
Copied!
dmatrix("cat", data=catdf)
dmatrix("cat", data=catdf)
Out[52]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept cat[T.B] cat[T.C]
1 0 0
1 1 0
1 0 1
1 0 1
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
'cat' (columns 1:3)
In [53]:
Copied!
dmatrix("C(cat)", data=catdf)
dmatrix("C(cat)", data=catdf)
Out[53]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept C(cat)[T.B] C(cat)[T.C]
1 0 0
1 1 0
1 0 1
1 0 1
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
'C(cat)' (columns 1:3)
In [54]:
Copied!
dmatrix("C(cat, Treatment)", data=catdf)
dmatrix("C(cat, Treatment)", data=catdf)
Out[54]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept C(cat, Treatment)[T.B] C(cat, Treatment)[T.C]
1 0 0
1 1 0
1 0 1
1 0 1
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
'C(cat, Treatment)' (columns 1:3)
In [55]:
Copied!
dmatrix("C(cat, Treatment('B'))", data=catdf)
# ALT. dmatrix("C(cat, Treatment(1))", data=catdf)
dmatrix("C(cat, Treatment('B'))", data=catdf)
# ALT. dmatrix("C(cat, Treatment(1))", data=catdf)
Out[55]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept C(cat, Treatment('B'))[T.A] C(cat, Treatment('B'))[T.C]
1 1 0
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 0 1
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
"C(cat, Treatment('B'))" (columns 1:3)
Avoiding perfect collinearity¶
In [56]:
Copied!
df_col = pd.DataFrame()
df_col["iscli"] = (doctors["work"] == "cli").astype(int)
df_col["iseld"] = (doctors["work"] == "eld").astype(int)
df_col["ishos"] = (doctors["work"] == "hos").astype(int)
df_col["score"] = doctors["score"]
df_col = pd.DataFrame()
df_col["iscli"] = (doctors["work"] == "cli").astype(int)
df_col["iseld"] = (doctors["work"] == "eld").astype(int)
df_col["ishos"] = (doctors["work"] == "hos").astype(int)
df_col["score"] = doctors["score"]
In [57]:
Copied!
formula_col = "score ~ 1 + iscli + iseld + ishos"
lm_col = smf.ols(formula_col, data=df_col).fit()
lm_col.params
formula_col = "score ~ 1 + iscli + iseld + ishos"
lm_col = smf.ols(formula_col, data=df_col).fit()
lm_col.params
Out[57]:
Intercept 36.718781 iscli 9.826673 iseld 14.396603 ishos 12.495504 dtype: float64
In [58]:
Copied!
lm_col.condition_number
lm_col.condition_number
Out[58]:
4496839867074116.0
In [59]:
Copied!
lm2.params
lm2.params
Out[59]:
Intercept 60.452901 alc -1.800101 weed -1.021552 exrc 1.768289 dtype: float64
Discussion¶
Other coding strategies for categorical variables¶
In [60]:
Copied!
dmatrix("0 + C(cat)", data=catdf)
dmatrix("0 + C(cat)", data=catdf)
Out[60]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
C(cat)[A] C(cat)[B] C(cat)[C]
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
0 0 1
Terms:
'C(cat)' (columns 0:3)
In [61]:
Copied!
dmatrix("1 + C(cat, Sum)", data=catdf)
dmatrix("1 + C(cat, Sum)", data=catdf)
Out[61]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept C(cat, Sum)[S.A] C(cat, Sum)[S.B]
1 1 0
1 0 1
1 -1 -1
1 -1 -1
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
'C(cat, Sum)' (columns 1:3)
In [62]:
Copied!
dmatrix("1+C(cat, Diff)", data=catdf)
dmatrix("1+C(cat, Diff)", data=catdf)
Out[62]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept C(cat, Diff)[D.A] C(cat, Diff)[D.B]
1 -0.66667 -0.33333
1 0.33333 -0.33333
1 0.33333 0.66667
1 0.33333 0.66667
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
'C(cat, Diff)' (columns 1:3)
In [63]:
Copied!
dmatrix("C(cat, Helmert)", data=catdf)
dmatrix("C(cat, Helmert)", data=catdf)
Out[63]:
DesignMatrix with shape (4, 3)
Intercept C(cat, Helmert)[H.B] C(cat, Helmert)[H.C]
1 -1 -1
1 1 -1
1 0 2
1 0 2
Terms:
'Intercept' (column 0)
'C(cat, Helmert)' (columns 1:3)
Exercises¶
EXX: redo comparison of debate and lectures scores¶
In [64]:
Copied!
students = pd.read_csv("datasets/students.csv")
lmcu = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(curriculum)", data=students).fit()
lmcu.tvalues.iloc[1], lmcu.pvalues.iloc[1]
students = pd.read_csv("datasets/students.csv")
lmcu = smf.ols("score ~ 1 + C(curriculum)", data=students).fit()
lmcu.tvalues.iloc[1], lmcu.pvalues.iloc[1]
Out[64]:
(-1.7197867420465645, 0.10917234443214417)
EXX: model comparison¶
In [65]:
Copied!
formula3w = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc + C(loc) + C(work)"
lm3w = smf.ols(formula3w, data=doctors).fit()
formula3 = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc + C(loc)"
lm3 = smf.ols(formula3, data=doctors).fit()
lm3w.compare_f_test(lm3)
formula3w = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc + C(loc) + C(work)"
lm3w = smf.ols(formula3w, data=doctors).fit()
formula3 = "score ~ 1 + alc + weed + exrc + C(loc)"
lm3 = smf.ols(formula3, data=doctors).fit()
lm3w.compare_f_test(lm3)
Out[65]:
(1.5158185269522728, 0.22299549360240853, 2.0)
The result is non-significant which means including the predictor C(work)
in the model is not useful.
EXX: run ANOVA test¶
In [66]:
Copied!
# Construct data as a pd.DataFrame
np.random.seed(42)
As = np.random.normal(0, 1, 20)
Bs = np.random.normal(-2, 1, 20)
Cs = np.random.normal(3, 1, 20)
Ds = np.random.normal(1.5, 1, 20)
dfABCD = pd.DataFrame()
dfABCD["group"] = ["A"]*20 + ["B"]*20 + ["C"]*20 + ["D"]*20
dfABCD["value"] = np.concatenate([As, Bs, Cs, Ds])
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(8,6)}):
ax = plot_lm_anova(dfABCD, x="group", y="value")
from scipy.stats import f_oneway
resABCD = f_oneway(As, Bs, Cs, Ds)
print(resABCD.statistic, resABCD.pvalue)
lmabcd = smf.ols("value ~ C(group)", data=dfABCD).fit()
lmabcd.fvalue, lmabcd.f_pvalue
# Construct data as a pd.DataFrame
np.random.seed(42)
As = np.random.normal(0, 1, 20)
Bs = np.random.normal(-2, 1, 20)
Cs = np.random.normal(3, 1, 20)
Ds = np.random.normal(1.5, 1, 20)
dfABCD = pd.DataFrame()
dfABCD["group"] = ["A"]*20 + ["B"]*20 + ["C"]*20 + ["D"]*20
dfABCD["value"] = np.concatenate([As, Bs, Cs, Ds])
with plt.rc_context({"figure.figsize":(8,6)}):
ax = plot_lm_anova(dfABCD, x="group", y="value")
from scipy.stats import f_oneway
resABCD = f_oneway(As, Bs, Cs, Ds)
print(resABCD.statistic, resABCD.pvalue)
lmabcd = smf.ols("value ~ C(group)", data=dfABCD).fit()
lmabcd.fvalue, lmabcd.f_pvalue
107.22963883851017 3.091116115443299e-27
Out[66]:
(107.22963883851006, 3.091116115443401e-27)
Links¶
- Patsy and Statsmodels https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iEANEcWqAx4
- Tests as LMs: https://lindeloev.github.io/tests-as-linear/
- https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/59047/how-are-regression-the-t-test-and-the-anova-all-versions-of-the-general-linear
- https://danielroelfs.com/blog/everything-is-a-linear-model/ via HN