Analysis of variance (ANOVA)#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
\(\def\stderr#1{\mathbf{se}_{#1}}\) \(\def\stderrhat#1{\hat{\mathbf{se}}_{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\Mean}{\textbf{Mean}}\) \(\newcommand{\Var}{\textbf{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\Std}{\textbf{Std}}\) \(\newcommand{\Freq}{\textbf{Freq}}\) \(\newcommand{\RelFreq}{\textbf{RelFreq}}\) \(\newcommand{\DMeans}{\textbf{DMeans}}\) \(\newcommand{\Prop}{\textbf{Prop}}\) \(\newcommand{\DProps}{\textbf{DProps}}\)
Definitions#
Formulas#
Example#
Explanations#
Discussion#
Equivalence between ANOVA and OLS#
via https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/175246/why-is-anova-equivalent-to-linear-regression
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import randint, norm
np.random.seed(124) # Fix the seed
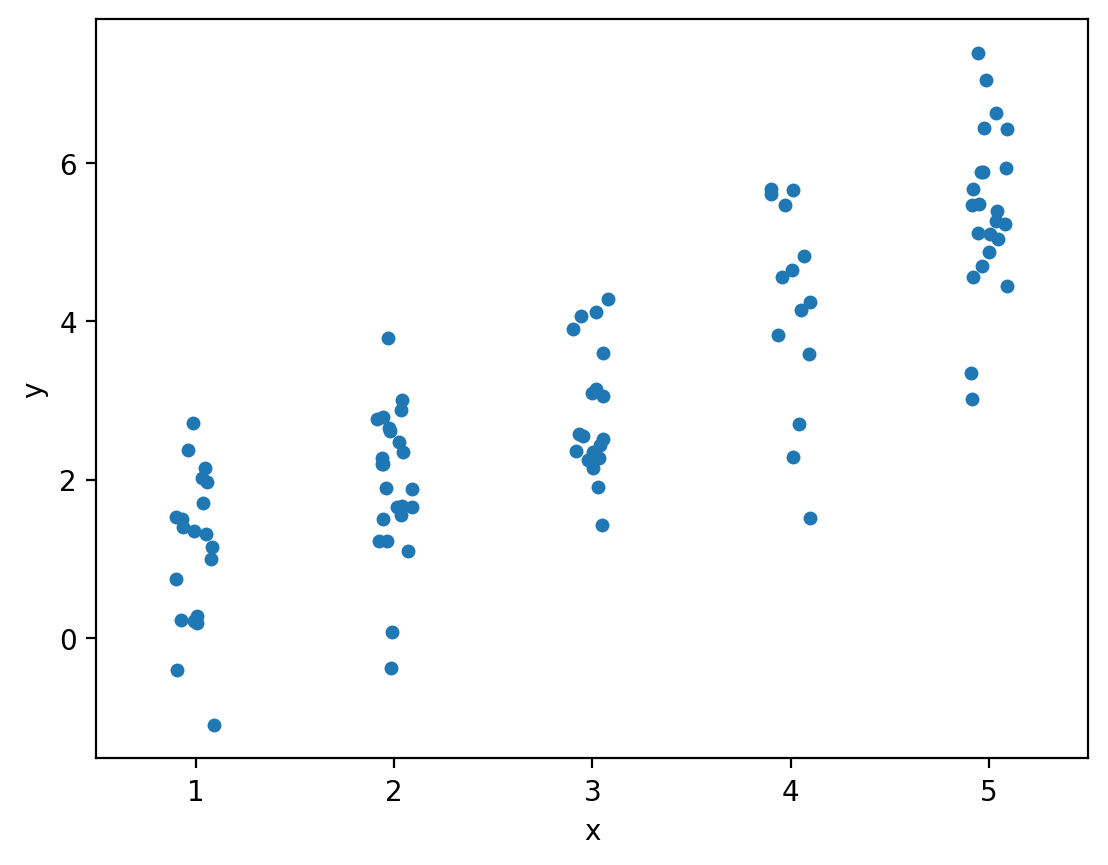
x = randint(1,6).rvs(100) # Generate 100 random integer U[1,5]
y = x + norm().rvs(100) # Generate my response sample
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
df = pd.DataFrame({"x":x, "y":y})
sns.stripplot(data=df, x="x", y="y")
df.groupby("x")["y"].mean()
# One-way ANOVA
from scipy.stats import f_oneway
x1 = df[x==1]["y"]
x2 = df[x==2]["y"]
x3 = df[x==3]["y"]
x4 = df[x==4]["y"]
x5 = df[x==5]["y"]
res = f_oneway(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5)
res
F_onewayResult(statistic=np.float64(62.07182379512491), pvalue=np.float64(1.113218183344844e-25))
import statsmodels.api as sm
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
# get ANOVA table as R like output
model = ols('y ~ C(x)', data=df).fit()
anova_table = sm.stats.anova_lm(model, typ=2)
anova_table
| sum_sq | df | F | PR(>F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(x) | 250.940237 | 4.0 | 62.071824 | 1.113218e-25 |
| Residual | 96.015072 | 95.0 | NaN | NaN |
# MEANS
# 1 1.114427
# 2 1.958159
# 3 2.844082
# 4 4.198083
# 5 5.410594
# Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) model
model = ols('y ~ C(x)', data=df).fit()
model.summary()
| Dep. Variable: | y | R-squared: | 0.723 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model: | OLS | Adj. R-squared: | 0.712 |
| Method: | Least Squares | F-statistic: | 62.07 |
| Date: | Mon, 09 Mar 2026 | Prob (F-statistic): | 1.11e-25 |
| Time: | 15:33:36 | Log-Likelihood: | -139.86 |
| No. Observations: | 100 | AIC: | 289.7 |
| Df Residuals: | 95 | BIC: | 302.7 |
| Df Model: | 4 | ||
| Covariance Type: | nonrobust |
| coef | std err | t | P>|t| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.1144 | 0.225 | 4.957 | 0.000 | 0.668 | 1.561 |
| C(x)[T.2] | 0.8437 | 0.304 | 2.772 | 0.007 | 0.239 | 1.448 |
| C(x)[T.3] | 1.7297 | 0.322 | 5.370 | 0.000 | 1.090 | 2.369 |
| C(x)[T.4] | 3.0837 | 0.350 | 8.802 | 0.000 | 2.388 | 3.779 |
| C(x)[T.5] | 4.2962 | 0.307 | 13.977 | 0.000 | 3.686 | 4.906 |
| Omnibus: | 3.712 | Durbin-Watson: | 1.985 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prob(Omnibus): | 0.156 | Jarque-Bera (JB): | 3.318 |
| Skew: | -0.444 | Prob(JB): | 0.190 |
| Kurtosis: | 3.084 | Cond. No. | 5.87 |
Notes:
[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.
betas = model.params.values
betas
array([1.11442735, 0.84373124, 1.72965468, 3.0836561 , 4.29616654])
scaled_batas = np.concatenate([[betas[0]], betas[0]+betas[1:]])
scaled_batas
array([1.11442735, 1.95815859, 2.84408203, 4.19808345, 5.41059388])
# Check if the two results are numerically equivalent
np.isclose(scaled_batas, df.groupby("x")["y"].mean().values)
array([ True, True, True, True, True])
# # Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) model (no intercept)
# model = ols('y ~ C(x) -1', data=df).fit()
# model.summary()
from scipy.stats.mstats import argstoarray
data = argstoarray(x1.values, x2.values, x3.values, x4.values, x5.values)
data.count(axis=1)
np.sum( data.count(axis=1) * ( data.mean(axis=1) - data.mean() )**2 )
np.float64(250.9402371658938)
# sswg manual compute
gmeans = data.mean(axis=1)
data_minus_gmeans = np.subtract(data.T, gmeans).T
(data_minus_gmeans**2).sum()
np.float64(96.01507202947789)
# sswg via parallel axis thm
gmeans = data.mean(axis=1)
np.sum( (data**2).sum(axis=1) - data.count(axis=1) * gmeans**2 )
np.float64(96.01507202947788)
from scipy.stats import f as fdist
def f_oneway(*args):
"""
Performs a 1-way ANOVA, returning an F-value and probability given
any number of groups. From Heiman, pp.394-7.
"""
# Construct a single array of arguments: each row is a group
data = argstoarray(*args)
ngroups = len(data)
ntot = data.count()
sstot = (data**2).sum() - (data.sum())**2/float(ntot)
ssbg = (data.count(-1) * (data.mean(-1)-data.mean())**2).sum()
sswg = sstot-ssbg
print(ssbg, sswg, sstot)
dfbg = ngroups-1
dfwg = ntot - ngroups
msb = ssbg/float(dfbg)
msw = sswg/float(dfwg)
f = msb/msw
prob = fdist.sf(dfbg, dfwg, f)
return f, prob
f_oneway(x1.values, x2.values, x3.values, x4.values, x5.values)
250.9402371658938 96.01507202947755 346.95530919537134
(np.float64(62.07182379512513), np.float64(1.697371507321727e-08))