Section 5.4 — Bayesian linear models#
This notebook contains the code examples from Section 5.4 Bayesian linear models from the No Bullshit Guide to Statistics.
See also examples in:
Notebook setup#
# load Python modules
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Figures setup
plt.clf() # needed otherwise `sns.set_theme` doesn"t work
from plot_helpers import RCPARAMS
RCPARAMS.update({"figure.figsize": (5, 3)}) # good for screen
# RCPARAMS.update({"figure.figsize": (5, 1.6)}) # good for print
sns.set_theme(
context="paper",
style="whitegrid",
palette="colorblind",
rc=RCPARAMS,
)
# High-resolution please
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = "retina"
# Where to store figures
DESTDIR = "figures/bayesian/lms"
<Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
# set random seed for repeatability
np.random.seed(42)
Simple linear regression using PyMC#
import pymc as pm
import numpy as np
import arviz as az
# Simulated data
np.random.seed(42)
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100)
y = 3 + 2 * x + np.random.normal(0, 1, 100)
# Bayesian Linear Regression Model
with pm.Model() as model:
# Priors
beta0 = pm.Normal("beta0", mu=0, sigma=10)
beta1 = pm.Normal("beta1", mu=0, sigma=10)
sigma = pm.HalfNormal("sigma", sigma=1)
# Likelihood
mu = beta0 + beta1 * x
y_obs = pm.Normal("y_obs", mu=mu, sigma=sigma, observed=y)
# Sampling
trace = pm.sample(2000, return_inferencedata=True)
WARNING (pytensor.tensor.blas): Using NumPy C-API based implementation for BLAS functions.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ImportError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[4], line 1
----> 1 import pymc as pm
2 import numpy as np
3 import arviz as az
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pymc/__init__.py:48
43 pytensor.config.gcc__cxxflags = augmented
46 __set_compiler_flags()
---> 48 from pymc import _version, gp, ode, sampling
49 from pymc.backends import *
50 from pymc.blocking import *
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pymc/gp/__init__.py:15
1 # Copyright 2024 The PyMC Developers
2 #
3 # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
(...)
12 # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 # limitations under the License.
---> 15 from pymc.gp import cov, mean, util
16 from pymc.gp.gp import (
17 TP,
18 Latent,
(...)
23 MarginalSparse,
24 )
25 from pymc.gp.hsgp_approx import HSGP, HSGPPeriodic
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pymc/gp/cov.py:52
29 from pytensor.tensor.variable import TensorConstant, TensorVariable
31 __all__ = [
32 "Constant",
33 "WhiteNoise",
(...)
49 "Kron",
50 ]
---> 52 from pymc.pytensorf import constant_fold
54 TensorLike = Union[np.ndarray, TensorVariable]
55 IntSequence = Union[np.ndarray, Sequence[int]]
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pymc/pytensorf.py:59
56 from pytensor.tensor.variable import TensorConstant, TensorVariable
58 from pymc.exceptions import NotConstantValueError
---> 59 from pymc.util import makeiter
60 from pymc.vartypes import continuous_types, isgenerator, typefilter
62 PotentialShapeType = Union[int, np.ndarray, Sequence[Union[int, Variable]], TensorVariable]
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pymc/util.py:21
18 from collections.abc import Sequence
19 from typing import Any, NewType, Optional, Union, cast
---> 21 import arviz
22 import cloudpickle
23 import numpy as np
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/arviz/__init__.py:34
30 _log = Logger("arviz")
33 from .data import *
---> 34 from .plots import *
35 from .plots.backends import *
36 from .stats import *
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/arviz/plots/__init__.py:2
1 """Plotting functions."""
----> 2 from .autocorrplot import plot_autocorr
3 from .bpvplot import plot_bpv
4 from .bfplot import plot_bf
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/arviz/plots/autocorrplot.py:7
5 from ..rcparams import rcParams
6 from ..utils import _var_names
----> 7 from .plot_utils import default_grid, filter_plotters_list, get_plotting_function
10 def plot_autocorr(
11 data,
12 var_names=None,
(...)
24 show=None,
25 ):
26 r"""Bar plot of the autocorrelation function (ACF) for a sequence of data.
27
28 The ACF plots are helpful as a convergence diagnostic for posteriors from MCMC
(...)
117 >>> az.plot_autocorr(data, var_names=['mu', 'tau'], max_lag=200, combined=True)
118 """
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/arviz/plots/plot_utils.py:15
11 from scipy.interpolate import CubicSpline
14 from ..rcparams import rcParams
---> 15 from ..stats.density_utils import kde
16 from ..stats import hdi
18 KwargSpec = Dict[str, Any]
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/arviz/stats/__init__.py:3
1 # pylint: disable=wildcard-import
2 """Statistical tests and diagnostics for ArviZ."""
----> 3 from .density_utils import *
4 from .diagnostics import *
5 from .stats import *
File /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/arviz/stats/density_utils.py:8
6 from scipy.fftpack import fft
7 from scipy.optimize import brentq
----> 8 from scipy.signal import convolve, convolve2d, gaussian # pylint: disable=no-name-in-module
9 from scipy.sparse import coo_matrix
10 from scipy.special import ive # pylint: disable=no-name-in-module
ImportError: cannot import name 'gaussian' from 'scipy.signal' (/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.20/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/scipy/signal/__init__.py)
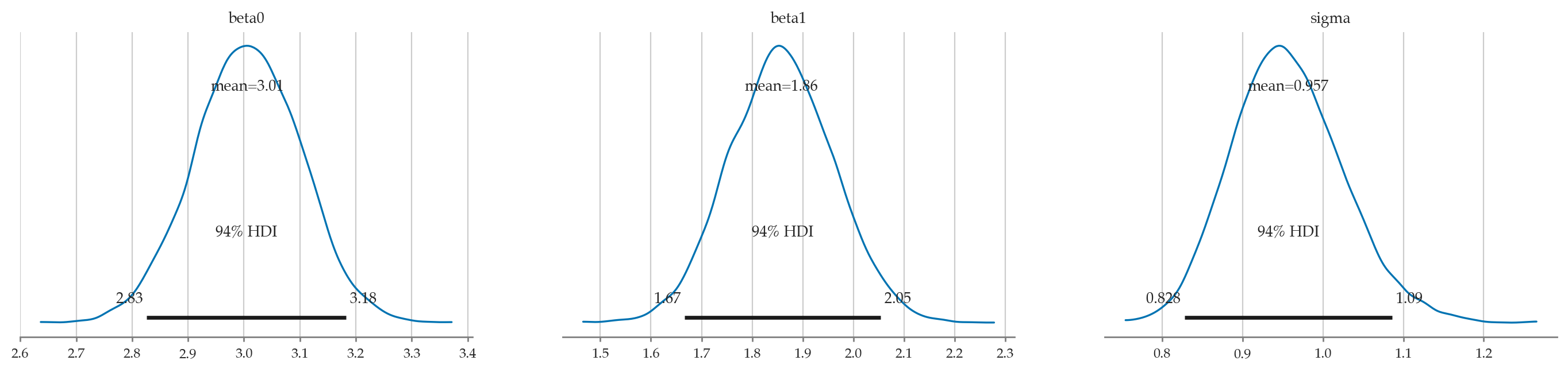
Summary using mean#
# Posterior Summary
summary = az.summary(trace, kind="stats")
summary
| mean | sd | hdi_3% | hdi_97% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| beta0 | 3.006 | 0.095 | 2.826 | 3.183 |
| beta1 | 1.857 | 0.104 | 1.667 | 2.054 |
| sigma | 0.957 | 0.069 | 0.828 | 1.086 |
Summary using median as focus statistic#
ETI = Equal-Tailed Interval
az.summary(trace, stat_focus="median", kind="stats")
| median | mad | eti_3% | eti_97% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| beta0 | 3.006 | 0.065 | 2.826 | 3.183 |
| beta1 | 1.856 | 0.070 | 1.666 | 2.053 |
| sigma | 0.953 | 0.046 | 0.837 | 1.096 |